Dealing with a pinched nerve can be a real pain – literally. Whether you’re experiencing the discomfort in your neck, back, or elsewhere, finding relief is a top priority. This comprehensive guide to pinched nerve treatment is your roadmap to saying goodbye to that nagging, persistent discomfort for good. From understanding the underlying causes and symptoms to exploring effective treatment options and preventive measures, we’ve got you covered.
Whether it’s a result of poor posture, injury, or repetitive motion, a pinched nerve can disrupt your daily life. But fear not, because in this guide, we’ll walk you through practical strategies and expert advice tailored to alleviate your discomfort and prevent future occurrences. Say hello to better mobility and improved quality of life as we delve into the most effective methods for pinched nerve treatment. It’s time to bid farewell to that pesky pinched nerve and embrace a life of comfort and vitality.
Understanding pinched nerves
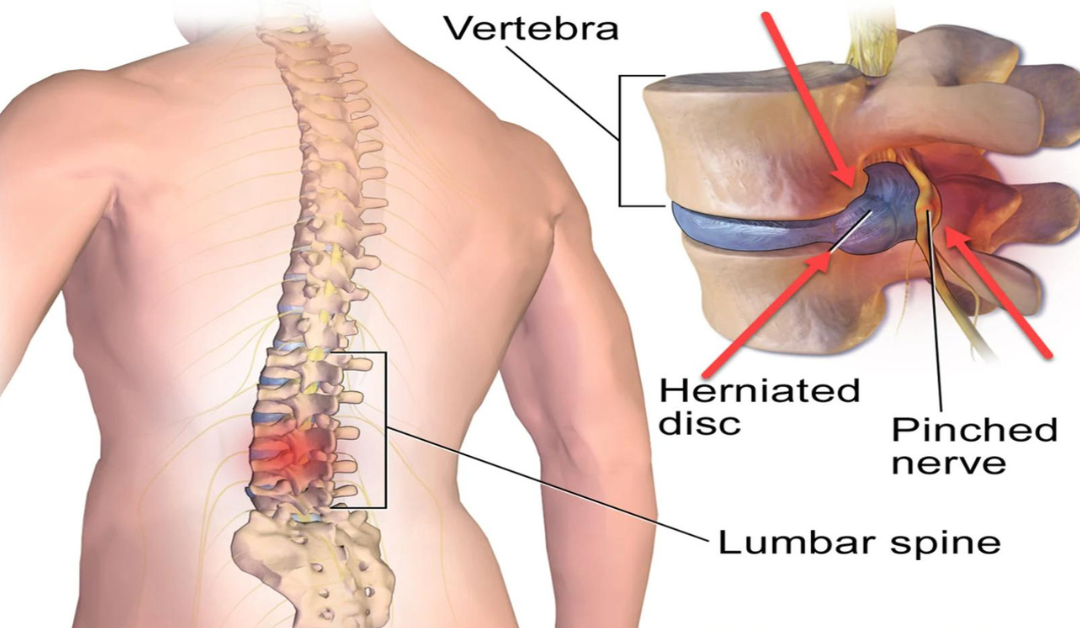
Understanding the nature of pinched nerves is crucial to effectively managing and treating the condition. A pinched nerve occurs when too much pressure is applied to a nerve by surrounding tissues, such as bones, cartilage, muscles, or tendons. This pressure disrupts the nerve’s function, leading to pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness. Pinched nerves can occur in various parts of the body, including the neck, lower back, wrists, and elbows. It’s essential to recognize the symptoms and seek appropriate treatment to alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications.
Pinched nerves can result from a variety of factors, including repetitive movements, poor posture, sports injuries, or conditions such as arthritis and obesity. Understanding the specific cause of your pinched nerve is essential for determining the most effective treatment approach. By identifying the underlying issue, you can work towards addressing the root cause and implementing targeted treatment strategies to achieve relief and promote long-term healing.
Accurate diagnosis of a pinched nerve is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. Healthcare professionals may utilize a combination of physical examinations, medical history assessments, and diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or nerve conduction studies to pinpoint the location and severity of the pinched nerve. With a clear understanding of the affected nerve and its underlying cause, personalized treatment options can be explored to address the discomfort and promote recovery.
Symptoms of a pinched nerve
Recognizing the symptoms of a pinched nerve is the first step towards seeking appropriate treatment and relief. Common symptoms may include localized pain that radiates outward, a tingling or “pins and needles” sensation, numbness, muscle weakness, or a burning sensation.
The specific symptoms experienced can vary depending on the location and severity of the pinched nerve. For example, a pinched nerve in the neck may lead to pain and tingling that extends into the arms, while a pinched nerve in the lower back may cause discomfort that radiates down the legs. It’s important to pay attention to these symptoms and seek medical guidance for proper evaluation and treatment.
Causes of pinched nerves
Pinched nerves can stem from a range of causes, each contributing to the compression and irritation of the affected nerve. One common cause is repetitive motion or overuse, which can lead to the compression of nerves in areas such as the wrists (carpal tunnel syndrome) or elbows (ulnar nerve entrapment).
Additionally, poor posture and spinal misalignment can contribute to the compression of nerves in the neck and lower back, resulting in discomfort and limited mobility. Injuries, such as herniated discs or fractures, can also lead to pinched nerves by exerting pressure on nearby nerve tissues. Furthermore, underlying health conditions like arthritis or diabetes can contribute to nerve compression, exacerbating symptoms and discomfort. Understanding the specific cause of your pinched nerve is essential for determining the most effective treatment approach.
Pinched nerve treatment options
The treatment of a pinched nerve often involves a multifaceted approach aimed at alleviating discomfort, promoting healing, and preventing future occurrences. Depending on the severity and underlying cause of the pinched nerve, various treatment options may be recommended.
Non-surgical treatments are typically explored as the initial approach, focusing on conservative methods to relieve symptoms and improve nerve function. These may include rest, activity modification, physical therapy, and medication to manage pain and inflammation. In cases where non-surgical interventions are insufficient, surgical options such as decompression or nerve release procedures may be considered to alleviate persistent symptoms and address the root cause of the pinched nerve.
Home remedies for pinched nerve relief
In addition to professional medical treatment, there are several home remedies and self-care strategies that can complement the management of a pinched nerve. Applying cold packs or warm compresses to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort. Gentle stretching exercises and targeted movements can promote flexibility and relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
Maintaining good posture and ergonomic practices, such as using supportive cushions or adjusting workspace setups, can also play a significant role in preventing aggravation of the pinched nerve. Furthermore, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods and supplements into your diet can support the body’s natural healing process and reduce nerve inflammation. By integrating these home remedies into your daily routine, you can actively contribute to the relief and recovery of a pinched nerve.
Physical therapy for pinched nerve treatment
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of non-surgical pinched nerve treatment, focusing on targeted exercises, manual techniques, and therapeutic modalities to alleviate symptoms and restore optimal nerve function. A skilled physical therapist can design a personalized rehabilitation program tailored to address the specific needs and limitations associated with your pinched nerve.
Through targeted exercises that improve strength, flexibility, and posture, physical therapy aims to alleviate pain, enhance mobility, and prevent future occurrences of nerve compression. Additionally, manual therapy techniques such as soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization can help release tension and reduce nerve impingement, contributing to improved comfort and function.
Surgical treatments for severe pinched nerves
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief or when severe nerve compression is present, surgical intervention may be recommended as a viable option. Surgical treatments for pinched nerves are designed to alleviate pressure on the affected nerve, address structural abnormalities, and promote long-term healing.
Common surgical procedures for pinched nerves include decompression surgeries, such as discectomy for herniated discs or carpal tunnel release for wrist nerve compression. These procedures aim to create space for the nerve and alleviate pressure, ultimately alleviating symptoms and restoring nerve function. Surgical treatments are typically considered when conservative measures have been exhausted, and the persistence of symptoms significantly impacts daily function and quality of life.
Preventing pinched nerves
Preventing the occurrence of pinched nerves is essential for maintaining optimal nerve health and overall well-being. Implementing proactive measures to reduce the risk of nerve compression can significantly contribute to long-term comfort and mobility. Maintaining proper posture and ergonomics, especially during prolonged periods of sitting or repetitive tasks, can help minimize unnecessary pressure on nerves.
Regular exercise and stretching routines that promote flexibility and strength can reduce the likelihood of muscular imbalances and nerve impingement. Additionally, practicing mindfulness of body mechanics and taking regular breaks to rest and stretch during repetitive activities can prevent the accumulation of stress on nerves. By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can minimize the risk of developing pinched nerves and enjoy improved nerve health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing the discomfort and limitations associated with a pinched nerve requires a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment approaches. By recognizing the underlying factors contributing to nerve compression and implementing targeted treatment strategies, individuals can alleviate discomfort, restore optimal nerve function, and prevent future occurrences.
From non-surgical interventions and physical therapy to surgical options for severe cases, a range of treatment modalities exists to address pinched nerves and promote long-term comfort and mobility. By embracing a proactive approach to preventive measures and incorporating home remedies and self-care strategies, individuals can actively contribute to the relief and recovery of pinched nerves. Ultimately, by arming ourselves with knowledge and implementing practical strategies, we can bid farewell to the discomfort of a pinched nerve and embrace a life of vitality and well-being.